Tuesday, December 23, 2014
Tuesday, February 25, 2014
Monday, November 18, 2013
Get Concurrent User list from IIS
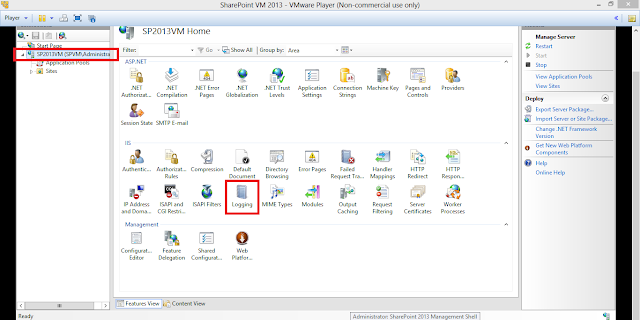
1. Enable the IIS Logs in the Server.
2. After Enable the log. Need to check whether the Fields are enabled or not.
3. Select your appropriate fields
4. After completed the above steps, need to install the “LogParser” tool to our server.
The log parser can be downloaded from the below location
5. Run “getConcurrentUser.bat” file.
code in bat file:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
cd\
c:
if exist c:\concurrentUser goto use_e
md concurrentUser
:use_e
cd C:\Program Files (x86)\Log Parser 2.2
set hr=%time:~0,2%
if "%hr:~0,1%" equ " " set hr=0%hr:~1,1%
set fdtm=%date:~-4,4%%date:~-10,2%%date:~-7,2%_%hr%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%
set fpath=c:\concurrentUser\userList_%fdtm%.csv
logparser -i:IISW3C -o:CSV "select distinct cs-username from C:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles\*.log" >%fpath% -recurse
Powershell.exe -executionpolicy remotesigned -File C:\britto\iislogdec\sendEmail.ps1 %fpath%
pause
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6. can able to get the output file from “c:\concurrentUser” path. This “CSV” file is generated in the name of “userList_<current Date and Time>.csv”
7. To send this report to email through power shell (save file name as sendEmail.ps1)
###########Define Variables########
$fromaddress = "bretto.be@gmail.com"
$toaddress = "bretto.be@gmail.com"
$bccaddress = "bretto.be@gmail.com"
$CCaddress = "bretto.be@gmail.com"
$Subject = "Concurrent user report"
#$body = get-content .\content.htm
$body = "Please find the Concurrent user report file"
$attachment =$args[0]
$smtpserver = "smtp.gmail.com"
####################################
$message = new-object System.Net.Mail.MailMessage
$message.From = $fromaddress
$message.To.Add($toaddress)
$message.CC.Add($CCaddress)
$message.Bcc.Add($bccaddress)
$message.IsBodyHtml = $True
$message.Subject = $Subject
$attach = new-object Net.Mail.Attachment($attachment)
$message.Attachments.Add($attach)
$message.body = $body
$smtp = New-Object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($SmtpServer, 587)
$smtp.EnableSsl = $true
$smtp.Credentials = New-Object System.Net.NetworkCredential("bretto.be@gmail.com", "xyz");
$smtp.Send($message)
#################################################################################
run the batch file we will get the mail with attachment.
Wednesday, November 13, 2013
Steps to Activate the custom timer job => Access denied when deploying a timer Job or activating a feature from SharePoint 2010 content web application
The following step i have used to followed to active the timer job.
Step 1: run the script in powershell command
function Set-RemoteAdministratorAccessDenied-False()
{
# load sharepoint api libs
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("Microsoft.SharePoint") > $null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("Microsoft.SharePoint.Administration") > $null
# get content web service
$contentService = [Microsoft.SharePoint.Administration.SPWebService]::ContentService
# turn off remote administration security
$contentService.RemoteAdministratorAccessDenied = $false
# update the web service
$contentService.Update()
}
Set-RemoteAdministratorAccessDenied-False
step 2: activate the timer job
feature in site collection feature.
Friday, August 10, 2012
SharePoint Branding
1. Sharepoint 2010 Fixed width Master Page Styling, no scrollbar issues.
Recently I have created my custom MasterPage in SharePoint Server. I have faced lots of issues to fix the fixed width. I have noticed when the Page load the SharePoint run the JavaScript function it search the <div> tag widh id #s4-workspace and it fix the width and height for the page.
I have searched in google and got a reference, using that refernce i have commented <div id="s4-workspace"> open tag and end tag. It was working fine but it gives problem while using some webparts, means it never suport chat and repots webparts. So, i get failed.
Again i googled and get nice reference, as per the reference i have overright some class, after that my page was looking good what i expected.
Steps for below:
1. I have create one .css file and added into siteassets library.
2. Then Open that css file in SPD (SharePoint designer)
3. The following styles are write in that css file:
html{
background-color:#55A0A7;
overflow/**/:auto;
}
background-color:#55A0A7;
overflow/**/:auto;
}
body.v4master {
width:1024px;
margin:0px auto;
overflow:visible;
background-color: transparent !important;
}
width:1024px;
margin:0px auto;
overflow:visible;
background-color: transparent !important;
}
.ms-dialog body.v4master {
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%;
}
body #s4-workspace {
left: 0;
overflow: auto !important;
overflow/**/: visible !important;
position: relative;
width: 100% !important;
display:table;
border-spacing:0px;
}
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%;
}
body #s4-workspace {
left: 0;
overflow: auto !important;
overflow/**/: visible !important;
position: relative;
width: 100% !important;
display:table;
border-spacing:0px;
}
.ms-dialog body #s4-workspace{
display:block !important;
overflow/**/: auto !important;
}
display:block !important;
overflow/**/: auto !important;
}
4. Then i have registed my css file into my custom MasterPage. like below line of code
<SharePoint:CssRegistration Name="SiteAssets/customStyle.css" runat="server" After="corev4.css" ></SharePoint:CssRegistration>
Wednesday, June 13, 2012
How to move Build file from one server to another server using Post Build Event in VS 2010
How to move
Build file from one server to another server using Post Build Event in Visual Studio 2010
1. Introduction
This document explains how to use How to move Build file from one server to another server using Post Build Event in VS 2010. The build file copy form source server to destination server with versioning. (i.e) here the version means we are creating a folder while build the solution with different name for each build.
2. How to add BAT file in project.
In you solution Right click the Project ==> In that Context menu click Add ==> Then Click New Item in sub menu.
Then the Template Window will be open. In this window in Left pane side Select Visual C# ==>
In the right Select TextFile ==> Give your filename with .bat extensionèthen click save
3. How to write commands in batch file
In your project you can able to see your newly added batch file. Open that batch file and add this below command in that file and save it.
@echo off
for /f "tokens=2* delims=:" %%a in ('echo %time%') do set mins=%%a
for /f "tokens=3* delims=:" %%a in ('echo %time%') do set sec=%%a
for /f "tokens=1* delims=." %%a in ('echo %sec%') do set secs=%%a
for /f "tokens=2* delims=." %%a in ('echo %sec%') do set mili=%%a
for /f "tokens=1* delims= " %%a in ('date/t') do set mmddyyyy=%%a
for /f "tokens=1* delims=." %%a in ('date/t') do set dd1=%%a
for /f "tokens=3* delims=." %%a in ('date/t') do set yyyy1=%%a
for /f "tokens=2* delims=." %%a in ('date/t') do set mm1=%%a
for /f "tokens=1* delims= " %%a in ('echo %yyyy1%') do set yyyy2=%%a
for /f "tokens=1* delims= " %%a in ('echo %~dp0') do set filePath=%%a
@echo on
SET date1=%yyyy2%%mm1%%dd1%%mins%%secs%%mili%
set filePath1=%filePath%
set solutionName=testBrTfs
xcopy "%filePath1%bin\debug\*.wsp" "\\DestinationServerName\SharedFolderName\%solutionname%\%date1%\"
4. How to write Post Build Event Command
Right click your project in your solution ==> then click property.
In this Build window Click Build Events ==> In the Post-build event Command line section write the below command
if $(ConfigurationName) == Release call "$(ProjectDir)ReleaseBuild.bat"
5. How to Release the Final Build
Before the final build your need to include the bin folder in that project and check out your “Release” folder in your project. And change the mode from “Debug” to “Release”
Thursday, June 7, 2012
SQL Server 2008 Two Node Cluster Installation and Setup
SQL Server 2008 Two Node Cluster Installation and Setup
The
installation process for SQL Server 2008 failover clusters has changed
significantly. Unlike earlier versions, when you install or upgrade a SQL
Server 2008 failover cluster, you must run the setup process for SQL Server
individually on each node of the failover cluster.
Installation Options for a SQL Server Failover Cluster
There
are two options for installing a SQL Server 2008 failover cluster: Integrated
and Advanced/Enterprise installation. Each option is designed to handle
different scenarios, although each option is capable of delivering exactly the
same end result. Both installation options are available in the SQL Server 2008
Setup Wizard and via command-prompt installation.
Integrated Installation
Integrated
installation satisfies the most common requirements for SQL Server deployments.
Integrated installation is used for creating a SQL failover instance, adding a
node to an existing cluster, and removing a node from an existing cluster regardless
of the original installation option.
SQL
Server integrated failover cluster installation consists of the following
steps:
- Create and configure a single-node SQL Server failover cluster instance. When configuration of the node is successful, you have a fully functional failover cluster instance. At this point, it does not have high availability because there is only one node in the failover cluster.
2.
On
each node to be added to the SQL Server failover cluster, run Setup with Add
Node functionality to add that node.
AS a prerequisite of setup routine for SQL Server 2008, before start
the activity couple of information should be in hand.
·
IP
address and server names for each node of the cluster
·
IP
addresses for the virtual SQL Server
·
IP
for MSDTC
·
SQL
Installation File location
·
Service
account details
·
Directory
details(Like which location should you place the SQL Server Program Files and DB data file)
·
Determine
instance name(s) and port number(s) .The SQL Server default port of 1433 but it
depends on company security policy.
·
Collation
settings and authentication mode (Most of the organization prefer default
collation and mixed mode authentication but some case it is changed depend
application requirement)
Prerequisites
for SQL 2008:
- .NET Framework 3.5 with Service Pack 1
- Windows Installer 4.5
Check the server to find out if these 2
prerequisites are on all nodes of the cluster.
If they are not you will need to download and apply to each node sql
server will reside.
a.
To check the server for these 2 programs go to:
·
Control Panel
·
Programs and Features
Find these on the Microsoft Site:
- .NET Framework 3.5 with Service Pack 1: http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=ab99342f-5d1a-413d-8319-81da479ab0d7&displaylang=en
- Windows Installer 4.5
Installing
a SQL Server 2008 Failover Cluster Using Integrated Installation with Add Node
Operation
1. After prerequisites are
installed, the Installation Wizard starts the SQL Server Installation Center.
To create a new cluster installation of SQL Server 2008, click New SQL
Server failover cluster installation on the Installation page.
2. The System Configuration
Checker runs a discovery operation on your computer. To continue, click OK.
You can view the details on the screen by clicking Show Details, or as
an HTML report by clicking View detailed report.
3. On the Product key page,
indicate whether you are installing a free edition of SQL Server, or whether
you have a PID key for a production version of the product
Note: The Product Key and License
Terms pages show up after the setup support files page if you already installed
the setup support files during a previous installation.
4. On the License Terms page,
read the license agreement, and then select the check box to accept the license
terms and conditions. Click Next to continue. To end Setup, click Cancel.
5. On the Setup Support Files
page, click Install to install the setup support files.
6. The System Configuration
Checker verifies the system state of your computer before Setup continues.
After the check is complete, click Next to continue. You can view the
details on the screen by clicking Show Details, or as an HTML report by
clicking View detailed report.
Correct any issues that are reported on
the rules list. Errors block Setup, but warnings do not. It is a best practice
to address all warnings and errors.
Example of Warning and Solution: In this example you can see that there is a
warning on the Network Binding Order. To fix this please complete the following
steps:
****MS
Link: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/955963
7. On the Feature Selection page,
select the components for your installation.
A description for each component group
appears in the right pane after you select the feature name. You can select any
combination of check boxes, but only the Database
Engine and Analysis Services support failover clustering. Other selected
components will run as stand-alone features without failover capability on the
current node that you are running Setup on.
You can specify a custom directory for
shared components by using the field at the bottom of this page. To change the
installation path for shared components, either update the path in the field
provided at the bottom of the dialog box, or click the ellipsis button to
browse to an installation directory. The default installation path is
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\.
Note: When you select the Database
Engine Services feature, both replication and full-text search are selected
automatically. Unselecting any of these subfeatures also unselects the Database
Engine Services feature.
8. On the Instance Configuration
page, specify whether to install a default or a named instance.
SQL Server Network Name — Specify a network name for
the new SQL Server failover cluster. This is the name that is used to identify
your failover cluster on the network.
Note: This is known as the virtual SQL
Server name in earlier versions of SQL Server failover clusters.
Instance ID — By default, the instance name is used
as the Instance ID. This is used to identify installation directories and
registry keys for your instance of SQL Server. This is the case for default
instances and named instances. For a default instance, the instance name and
instance ID would be MSSQLSERVER. To use a non-default instance ID, select the Instance
ID box and provide a value.
Note: Typical stand-alone instances
of SQL Server 2008, whether default or named instances, do not use a nondefault
value for the Instance ID box.
Instance root directory — By default, the instance
root directory is C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\. To specify a
nondefault root directory, use the field provided, or click the ellipsis button
to locate an installation folder.
Detected SQL Server instances and
features on this computer
- The grid shows instances of SQL Server that are on the computer where Setup
is running. If a default instance is already installed on the computer, you
must install a named instance of SQL Server 2008. Click Next to
continue.
9. The Disk Space Requirements
page calculates the required disk space for the features that you specify, and
it compares requirements to the available disk space on the computer where
Setup is running.
10. Use the Cluster Resource Group
page to specify the cluster resource group name where SQL Server virtual server
resources will be located. To specify the SQL Server cluster resource group
name, you have two options:
·
Use
the drop-down box to specify an existing group to use.
·
Type
the name of a new group to create.
11. On the Cluster Disk Selection
page, select the shared cluster disk resource for your SQL Server failover
cluster.
The cluster disk is where the SQL Server
data will be stored. More than one disk can be specified. The Available shared disks box displays a
list of available disks, whether each is qualified as a shared disk, and a
description of each disk resource. Click Next to continue.
Note: The first drive is used as the
default drive for all databases, but it can be changed on the Database Engine
or Analysis Services configuration pages.
12. On the Cluster Network
Configuration page, specify the network resources for your failover cluster instance:
·
Network
Settings —
Specify the IP type and IP address for your failover cluster instance. On
Windows Server 2008 failover clusters, SQL Server supports the use of DHCP
addresses. Before choosing this option make sure that any network security such
as firewalls and IPsec in use between this SQL Server and its clients can
accommodate server side DHCP. For example, some firewalls will require a static
port for proper configuration of the firewall.
Click Next to continue.
13. Use the following page to specify
the security policy for the cluster.
The following screenshot displays the
cluster security policies for Windows Server 2003. In Windows Server 2003, you
can not leverage service SIDs. Specify domain groups for SQL Server services.
All resource permissions are controlled by domain-level groups that include SQL
Server service accounts as group members. This is displayed in the following
screen shot.
The following screenshot displays the
cluster security policies available for Windows Server 2008. In Windows Server
2008 and later versions, service SIDs (server security IDs) are the recommended
and default setting. The option to specify domain groups is available but not
recommended. For information about service SIDs functionality on Windows Server
2008, see Setting Up Windows Service
Accounts (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143504.aspx).
This is displayed in the following screen shot.
Click Next to continue.
Note: If you are installing a SQL
Server 2008 failover cluster instance in a Windows 2000 Server mixed-mode
domain, you must use domain global groups for SQL Server clustered services.
Note: Windows 2000 Server domain
controllers can operate in mixed mode or native mode. Mixed mode enables
down-level domain controllers in the same domain.
Work flow for the rest of this procedure
depends on the features that you have specified for your installation. You
might not see all the pages, depending on your selections (Database Engine,
Analysis Services, or Reporting Services).
14. On the Service Accounts tab, specify login accounts for SQL Server
services. The actual services that are configured on this page depend on the
features that you are installing.
You can assign the same login account to
all SQL Server services, or you can configure each service account
individually. The startup type is set to manual for all cluster-aware services,
including full-text search and SQL Server Agent, and cannot be changed during
installation. Microsoft recommends that you configure service accounts
individually to provide least privileges for each service, where SQL Server
services are granted the minimum permissions they have to have complete their
tasks..
15. To specify the same login
account for all service accounts in this instance of SQL Server, provide
credentials in the fields at the bottom of the page.
Security note: Do not use a blank password.
Use a strong password.
18.
When
you are finished specifying login information for SQL Server services, click Next.
19.
Use
the Collation tab to specify nondefault collations for the Database
Engine and Analysis Services.
16. Use the Account Provisioning tab to specify the following:
·
Authentication
mode - select Windows authentication or Mixed Mode authentication for your
instance of SQL Server. If you select Mixed Mode authentication, you must
provide a strong password for the built-in SQL Server system administrator
account.
·
·
SQL
Server administrators - You must specify at least one system administrator for the
instance of SQL Server. To add the account under which SQL Server Setup is
running, click Add Current User. To add or remove accounts from the list
of system administrators, click Add or Remove, and then edit the
list of users, groups, or computers that will have administrator privileges for
the instance of SQL Server.
When you are finished editing the list,
click OK. Verify the list of administrators in the configuration dialog
box. When the list is complete, click Next.
17. Use the Data Directories tab to specify nondefault installation
directories. To install to default directories, click Next.
Important: If you specify nondefault
installation directories, make sure that the installation folders are unique to
this instance of SQL Server. None of the directories in this dialog box should
be shared with directories from other instances of SQL Server. The data
directories should be located on the shared cluster disk for the failover
cluster.
18. Use the FILESTREAM tab to enable FILESTREAM for your instance of SQL
Server.
Click Next to continue.
19. On the Analysis Services
Configuration page, use the Account Provisioning tab to specify users or
accounts that will have administrator permissions for Analysis Services. You
must specify at least one system administrator for Analysis Services. To add
the account under which SQL Server Setup is running, click Add Current User.
To add or remove accounts from the list of system administrators, click Add
or Remove, and then edit the list of users, groups, or computers that
will have administrator privileges for Analysis Services.
When you are finished editing the list,
click OK. Verify the list of administrators in the configuration dialog
box. When the list is complete, click Next.
20. Use the Data Directories tab to specify nondefault installation
directories. To install to default directories, click Next.
Important: If you specify nondefault
installation directories, make sure that the installation folders are unique to
this instance of SQL Server. None of the directories in this dialog box should
be shared with directories from other instances of SQL Server. The data
directories should be located on the shared cluster disk for the failover
cluster.
21. Use the Reporting Services
Configuration page to specify the kind of Reporting Services installation to
create. For failover cluster installation, the option is set to “Install, but
do not configure the report server.” You must configure Reporting Services
after you complete the installation.
22. On the Error and Usage Reporting
page, specify the information that you want to send to Microsoft that will help
improve SQL Server. By default, options for error reporting and feature usage
are disabled.
23. The System Configuration
Checker runs one more set of rules to validate your configuration with the SQL
Server features that you have specified.
24. The Ready to Install page
displays a tree view of installation options that you specified during Setup.
To continue, click Install.
25. During installation, the
Installation Progress page provides status so that you can monitor installation
progress as Setup continues.
26. After installation, the Complete page provides a link to the
summary log file for the installation and other important notes. To complete
the SQL Server installation process, click Close.
High-Availability
1. We now have a fully
functioning SQL Server 2008 failover cluster but there is only one Node to this
SQL Server instance. To make this
High-Availability we will need to add a node to this sql server instance.
2. Before we start adding a node to this sql
instance we need to apply the service pack to this node.
Applying SQL Server Service Pack and/or Hot Fix to base node:
Next you will install the latest Service Pack, which will be found in
the D:\SQL\ directory
1. Click on the .exe for the correct service
pack make sure you have the right versions:
X86 or X64
3. At the Welcome Screen make sure that
everything passes or have warnings. If
anything has failed here you have to fix before moving forward.
4. At the License Terms: Click I
Accept The License Terms. Then Click
Next
5. Select
Features: Select the part you want
to apply service pack to if it is not already selected. Then Click Next.
6. Check
Files In Use: There is nothing that
needs to be done here at this point.
Just click Next. *****If for some
reason you cannot restart the node that you are applying sql server to you will
need to manually stop the service to avoid a computer restart.
7. Ready to Update: Check to make sure all updates
are correct and then Click: Update
8. Update Progress: Monitor the update Progress. Once it is complete if it is successful you
can click Next.
9.
Complete: The next screen will
give you details about the install as well as Summary log if you want to view
the install log. If the service pack
fails you can click this link to find out any info about why.
High-Availability
1. We now have a fully functioning SQL Server
2008 failover cluster but there is only one Node to this SQL Server
instance. To make this High-Availability
we will need to add a node to this sql server instance.
2. The
number of nodes you can add in a failover cluster depends on the editions of
SQL Server that you will use. A Standard
Edition of SQL Server 2008 can support up to two (2) nodes in a failover cluster while the Enterprise
Edition supports up to sixteen (16) nodes
Adding a Node to a Failover Instance
SQL
Server 2008 provides specific installation steps to incorporate a node within
the cluster as a potential node for a SQL Server failover instance to run on.
To add a cluster node that is not already configured as part of a SQL Server
instance, you must run setup on the node to add it to the SQL Server failover
instance. This process copies the binaries to the local node and configures the
node to be part of the SQL Server cluster. By default, when a node is added to
a failover cluster, it is added to the end of the list of the available nodes
and becomes available for failover.
Setup
does not install .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 on a clustered operating system. You
must install .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 before you run Setup.
You
may need to apply cumulative updates to the original media before you install
SQL Server 2008, if you are affected by a known issue in the Setup program. For
more information about known issues and detailed instructions, see How to update or slipstream an
installation SQL Server 2008 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/955392).
Note
that setup operations for SQL Server failover clustering have changed in this
release. To install or upgrade a SQL Server failover cluster, you must run the
Setup program on each node of the failover cluster.
To
add a node to an existing SQL Server failover cluster, you must run SQL Server
Setup on the node that is to be added to the SQL Server failover cluster
instance. Do not run Setup on the active node.
To
remove a node from an existing SQL Server failover cluster, you must run SQL
Server Setup on the node that is to be removed from the SQL Server failover
cluster instance.
To Add a Node to an Existing SQL Server 2008 Failover Cluster
1.
Insert
the SQL Server installation media, and from the root folder, double-click
Setup.exe. To install from a network share, navigate to the root folder on the
share, and then double-click Setup.exe. You may be asked to install the
prerequisites if they are not previously installed.
Install Windows Installer 4.5. Windows
Installer 4.5 is required, and it can be installed by the Installation Wizard.
If you are prompted to restart your computer, restart, and then start SQL
Server 2008 Setup.exe again.
2.
When
prerequisites are installed, the Installation Wizard will launch the SQL Server
Installation Center. To add a node to an existing failover cluster instance,
click Installation in the left-hand pane. Then, click Add node to a
SQL Server failover cluster.
The System Configuration Checker will run
a discovery operation on your computer. To continue, click OK. Setup log
files have been created for your installation. For more information about log
files, see How
To: View SQL Server Setup Log Files
(http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143702.aspx).
3.
On
the Product Key page, specify the PID key for a production version of the
product. Note that the product key you enter for this installation must be for
the same SQL Server 2008 edition as that which is installed on the active node.
Note: The Product Key and License
Terms pages show up after the setup support files page if you already installed
the setup support files during a previous installation.
4.
On
the License Terms page, read the license agreement, and then select the check
box to accept the licensing terms and conditions. To continue, click Next.
To end Setup, click Cancel.
5.
On
the Setup Support Files page, click Install to install the setup support
files. To install prerequisites, click Install.
6.
The
System Configuration Checker will verify the system state of your computer
before Setup continues. After the check is complete, click Next to
continue.
7.
On
the Cluster Node Configuration page, use the SQL Server instance name box to specify the name of the SQL Server
2008 failover cluster instance that will be modified during this setup
operation.
8.
On
the Service Accounts page, specify login accounts for SQL Server services. The
actual services that are configured on this page depend on the features you
selected to install. For failover cluster installations, account name and
startup type information will be prepopulated on this page based on settings
provided for the active node. You must provide passwords for each account.
Security note: Do not use a blank password. Use a
strong password.
When you are finished specifying login
information for SQL Server services, click Next.
9.
On
the Error and Usage Reporting page, specify the information to send to
Microsoft that will help to improve SQL Server. By default, options for error
reporting and feature usage are enabled.
10.
The
System Configuration Checker will run one more set of rules to validate your
computer configuration with the SQL Server features you have specified.
11.
The
Ready to Add Node page displays a tree view of installation options that you
specified during setup.
12.
The
Add Node Progress page provides status so you can monitor add node progress as
Setup proceeds.
13.
After
installation, the Complete page provides a link to the summary log file for the
installation and other important notes. To complete the SQL Server installation
process, click Close.
14. If you are instructed to
restart the computer, do so now. It is important to read the message from the
Installation Wizard when you are done with setup.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)